Home / Nose Sinuses / Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction (ETD)
Call +65 8125 3580
for 24 by 7 appointment
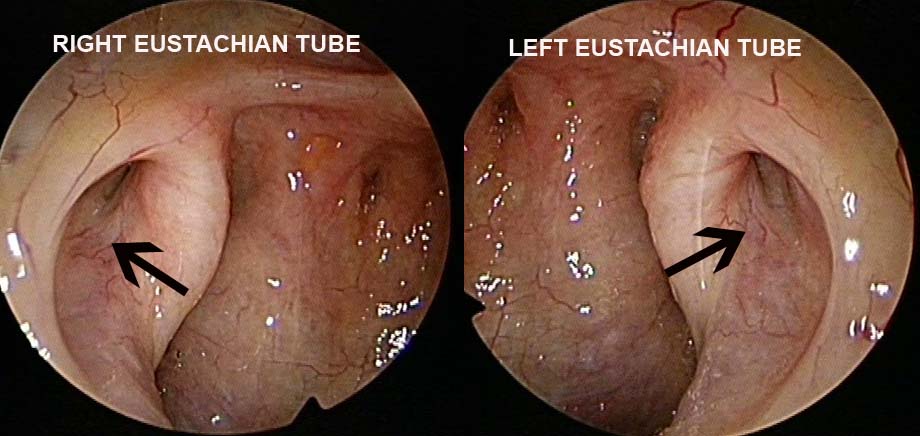
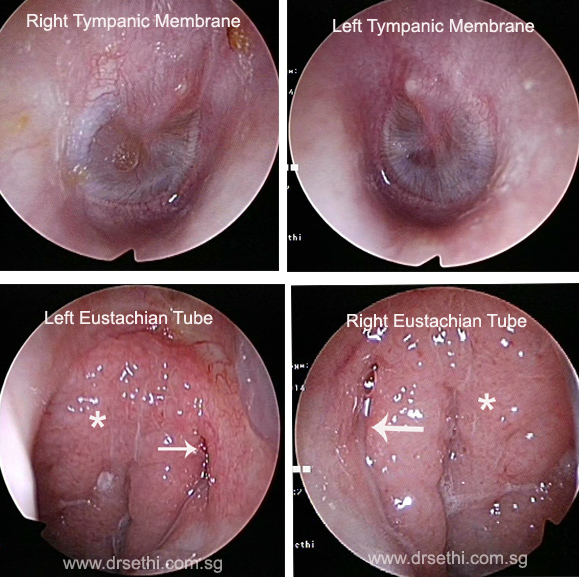
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear with the nasopharynx or an area behind the nose called the postnasal space. The opening of the eustachian tube in the post nasal space can be visualised with the endoscope. The main function of the eustachian tube is to equalise the pressure in the middle ear to the same as the atmosphere. This is achieved by the muscles of the eustachian tube which contract and relax in doing so. This eustachian tube function can be compromised when there is oedema or swelling in or around the its openings. The oedema may be a result of allergic rhinitis, inflammation in the nasopharynx due to smoking or infection. In children, a common cause of blocked eustachian tubes is the enlargements of adenoids. As a result of the blockage of the eustachian tube a negative pressure develops in the middle ear. Prolonged negative middle ear pressure lead to fluid accumulation or “glue ears” resulting in a conduction hearing loss. In the image, you can see that the eustachian tube on both sides (white arrow) are blocked by the inflammed nasopharynx (white asterisk). As a result fluid accumulated in the middle ear on both sides Symptoms of eustachian tube dysfunction or blockage are, sensation of a “blocked” ear, echoing sensation, ringing sensation in the ears and hearing loss. These symptoms can sometimes be early symptoms of nose cancer where the muscles of the eustachian tubes are effaced with the cancer.

Not sure if you are experiencing eustachian tube dysfunction? Speak to A/Prof Sethi to find out if this is the medical condition you are having at +65 8125 3580. Or book an appointment with A/Prof Sethi for a consultation on your symptoms and treatment options.
